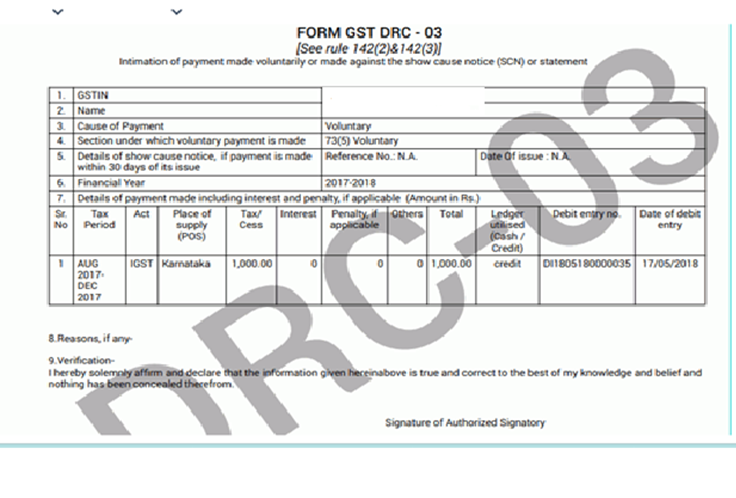
Clause 44 It was added w.e.f 20th August 2018 but Reporting under this clause was deferred till 31st March 2019 vide Circular No. 6/2018 dated 17th August 2018, So reporting in clause 44 is started from AY 2019-20.
The Objective for insertion of this Clause 44:
The main objective is to co-relate GST Data with Income Tax Data.
FAQ’s on CLAUSE 44
Q.1. Is reporting in this clause applicable only for Assessee who are GST registered?
Ans: No, Reporting is to be made by all assesses who are registered under GST or not.
Q.2. Interpretation of wordings “Breakup of total expenditure”? What expenditures are not Included?
Ans: Interpretation should be “broader” with reference to Capital Expenditure as well as Revenue Expenditure including Purchases.
But activities or transactions which those neither as a supply of goods nor a supply of services and thus expenditure incurred in respect of such activities need not be reported under this clause.
1. Salary not Included
2. Depreciation under section 32, deduction for bad debts u/s 36(1)(vii) etc. which are not expenses should not be reported under this clause.
3. Bad Debts written off etc.,
So we can say any expenditure that is incurred, wholly and exclusively for the business or profession of the assessee qualifies for the deduction under the Act.
Q.3. Tabular format for disclosure:
| Sl. No. | Total amount of Expenditure incurred during the year | Relating to Goods or services Exempt from GST | Relating to entities Falling under Composition Scheme | Relating to Other Registered Entities | Total Payment to Registered Entities | Expenditure relating to entities not registered under GST |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) |
The format as per clause 44 of form 3CD requires that the information is to be given as per the following details:
A. Total amount of expenditure incurred during the year
B. Expenditure in respect of entities registered under GST
C. Expenditure related to entities not registered under GST
the expenditure in respect of entities registered under GST is further sub-classified into four categories as follows:
a) Expenditure relating to goods or services exempt from GST
b) Expenditure relating to entities falling under the composition scheme
c) Expenditure relating to other registered entities
d) Total payment to registered entities
Q.4. Colum 2 says “Total amount of Expenditure incurred during the year” so shall we report head-wise / nature wise expenditure?
Ans: The heading of the table which starts with the words “Breakup of total expenditure” and hence the total expenditure including purchases as per the above format may be given. It appears that head-wise / nature wise expenditure details are not envisaged in this clause.
However, it is recommended to take head wise/nature wise expenditure details as a part of working paper of the Audit.
Q.5. What are the Expenditure relating to other registered entities (column 5)?
Ans: The value of all inward supplies from registered dealers, other than supplies from composition dealers and exempt supply from registered dealers, are to be mentioned in this column.
Q.6. What is the meaning of “Total payment to registered entities (column 6)”?
Ans: The language used in sub-heading of column 6 is total’ payment’ to registered entities. The word ‘payment’ should harmoniously be interpreted as ‘expenditure’ as the combined heading of columns (3), (4), (5) is ‘Expenditure in respect of entities registered under GST’. Hence, the total expenditure in respect of registered entities i.e., sum total of values reported in columns (3), (4) and (5) should be reported in Column 6.
Q.7. Checks and Control while reporting?
Ans: There are some checks and control so auditor make sure on correctness on reporting.
- Amount of Serial number 2 is equal to amount of serial number 6 PLUS Serial number 7.
- Amount of Serial number 6 is equal to amount of serial number 3 PLUS Serial number 4 PLUS Serial number 5.
| Total Value of Expenditure in P & L for the year | XXX |
| Add: Total Value Capital Expenditure Not Included in P & L | XXX |
| Less: Total Value Of non-cash Charges considered as expenditure | XXX |
| Less: Total Value of Expenditure Excluded For being Transactions in securities and Transactions In money | XXX |
| Less: Total value Of Expenditure Excluded by virtue of Schedule III to the CGST Act,2017 | XXX |
| Balance being Value of Expenditure for clause 44 | XXX |